What are KPIs? Guidelines for Building and Applying KPIs in Businesses
I. What is KPI? Why Do You Need KPIs?
KPI (short for Key Performance Indicator) is a job performance evaluation indicator, reflecting the level of completion of individual, departmental or enterprise goals. KPIs are expressed through different figures, ratios, quantitative indicators, etc., by the professional characteristics of each object.
In businesses, KPIs are often built at different levels to both serve as goals and measure progress and results.
High-level KPIs will focus on common strategic goals such as: Increasing 120% of total revenue in October, Completing 35 provincial projects in the fourth quarter,...
In contrast, low-level KPIs are used for process systems, individuals, and departments, to evaluate the performance of individual jobs. For example, of an IT business: The level of web maintenance and troubleshooting within 24 hours from the time of occurrence (except for force majeure cases)
Benefits of applying KPI in business:
With leaders and management levels:
- Monitor employee performance intuitively, transparently, and accurately as well as propose appropriate salary, reward, and discipline regimes.
- Improve the efficiency of the work acceptance process
- Ensure goals and visions can be completed as expected
With staff:
- Understand the level of completion of the work compared to the set goals
- Motivate to work towards achieving goals
- Detecting defects if the task is behind schedule for timely improvement
II. Common Mistakes When Building KPI
Based on the definition of what KPI is and the examples of KPIs above, we will go into understanding the mistakes in KPI construction that businesses often make. These include:
1. KPIs are not linked to the strategic goals of the business
As the name suggests, KEY Performance Indicators and KPIs must be IMPORTANT indicators. More specifically, they must be built and tracked based on the strategic goals of each department and business. Developing and evaluating KPIs that are not in line with specific goals can cause businesses to waste resources and resources, and not bring the expected results.
Going back to the example above, with a website introducing products with the goal of selling and increasing revenue, the KPI indicator to increase customer conversion rate given is completely reasonable. On the contrary, metrics such as the number of page visitors, page view time, etc., although important, are used to evaluate website quality, but will not be considered KPIs because there is no relationship. closely related to the intended purpose.
2. Focus only on the resulting KPIs and ignore the leading KPIs
KPIs like “Increase website sales conversion rate by 20%” are metrics that measure the result, but don't show us the cause for this result. Invisible, this indicator will become ambiguous and difficult to achieve without building a set of KPIs representing additional causes (For example, in this case, it could be “Launching 3 new products of the year”).
In general, there should be a close cause-and-effect relationship between KPIs. Businesses should therefore also balance between the two types of KPIs on results and causes to ensure the expected outputs.
3. Build fixed KPIs, no updates and customization over time
Continuing to follow up from the above example, for example, with only half the expected time of 3 months, the sales conversion rate has reached the threshold of 20%, now what should the business do?
(1) Keep KPIs unchanged and let employees relax and lose motivation to strive for work for the rest of the time?
(2) Or customize KPIs to match the development momentum of the website and the business?
The answer is probably relatively simple because no one wants to waste their resources and stagnate when they have strong growth momentum. Therefore, the KPI will now be customized to match the actual situation of the business. Similarly, when it comes to difficult times, the evaluation indicators should also be optimized to ensure that employees can handle the work reasonably and effectively.
* Note, that KPIs should not be applied to measure the results of goals in the creative field.
The job characteristics of creative positions such as designer painters, software developers, architects, data analysts, etc. are jobs, with the goal of continuous innovation, no repetition, There are even things that happen exactly once or in a short time, so KPIs cannot be applied. In these cases, the OKR (Objectives & Key Results) model is the right choice. More and more companies are applying OKR in goal management and internal operations such as Intel, Google, LinkedIn, Deloitte,...
III. Instructions On How to Build and Apply KPIs in The Business
Step 1: Identify the department/KPI builder
There are 2 main methods:
Method 1: The functional departments/departments build their KPI system for positions in their department/department; in which the human resource management team plays a supporting role, guiding methods to ensure that KPIs comply with the above principles. According to this method, the person who develops the KPI is usually the Head of the department/department/department – the person who has the best understanding and overview of the tasks and requirements of the positions and titles in the department. The larger the department/Department/Department, the more subdivided the KPI development is for subordinates.
- Advantages: KPIs will be highly feasible and clearly show the functions and tasks of the department.
- Disadvantages: if the department sets its own goals, there will often be a lack of objectivity, setting goals too low. The advice is that if using this method, it is necessary to have the assessment and evaluation of the human resources team and senior management team.
Method 2: In the human resources department, the senior management team will provide a set of KPIs for the department/department/department. Unlike the above method, this method ensures the objectivity and science of the method. However, the given KPIs may not be realistic, not properly representing the functions and duties of the department/department/department. To overcome this problem, the KPI system, after being built, needs the appraisal and evaluation of the functional department.
Step 2: Identify KPIs
The most important factor when building KPIs is to make sure they are closely aligned with the specific goals of the department or business. This can be illustrated by the following model:
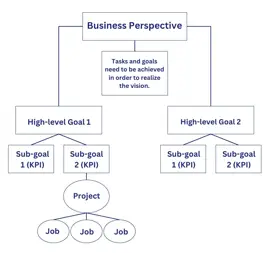
After you have agreed on KPIs with the goals of the department or business, the next step is to apply SMART criteria to evaluate each performance indicator:
S – Specific: Specific goal
M – Measurable: Measurable goal
A – Attainable: An achievable goal
R – Relevant: Realistic Goals
T – Timebound: The goal has a specific deadline
- If the KPIs built do not meet the SMART criteria, it will not only adversely affect the evaluation in particular but also have negative consequences for the organizational management system in general.
- If the target does not meet specific criteria (Specific), the employee does not know what to do and how to achieve the desired work efficiency.
- Indicators are not measurable, the performance results will not be meaningful
- If KPIs are not achievable (Achievable) or unrealistic (Realistic), the goal is too far away, employees cannot achieve it despite their best efforts. This affects psychologically, causing fatigue, depression, and lack of motivation to work.
- The KPIs do not have a specific limit (Time-bound) so employees do not know how long this work must be done or when it must be completed; which makes it difficult to control what they're doing.
Also, note that the performance metrics selected as KPIs will vary depending on the business type, employee-specific activities, and general departmental KPIs. For example, KPIs can be used to measure areas such as units sold, profit per item, product quality, customer service, the time needed to complete tasks, customer referrals, employee turnover,...
Even roles that seem unlikely to contribute to the financial growth of the business need KPIs that align with the goals and future of the business
For example, the KPI for the technical department is to improve the quality of the internet connection.
Taking an example from a business's Marketing activity, more specifically a product introduction website, a KPI can be built as follows:
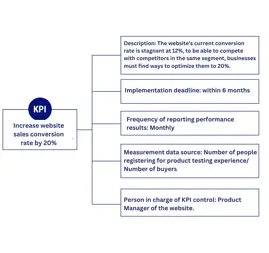
KPI: Increase website sales conversion rate by 20%
- Description: The current conversion rate of the website is stalled at 12%, to compete with competitors in the same segment, businesses must find ways to optimize them to 20%.
- Implementation period: within 6 months.
- Performance reporting frequency: Monthly
- Measurement data source: Number of people who sign up for a product trial / Number of shoppers
- Person in charge of controlling KPI: Product Manager of the website.
Step 3: Evaluate KPI completion
After successfully building KPIs for departments and job positions in the business, it's time to apply them to management, both human resources and productivity.
Because KPIs have been defined based on measurable criteria, there is certainly a specific evaluation method for each KPI item. In general, every job and KPI can be divided into 3 main groups as follows:
Group A: takes a lot of time to implement, and greatly affects the common goal.
Group B: takes little time to implement, affects a lot of the common goal OR/AND takes a lot of time to implement, has little impact on the common goal.
Group C: takes less time, less impact.
Each of these KPIs will have a different weight, depending on their importance, such as A: 50%; B: 30%, and C: 20%
To evaluate the completion level of an employee A has a set of 3 KPIs including A, B, and C; where KPI C has 2 children KPIs, we can use the following formula:

Step 4: Relationship between KPI assessment and salary bonus
For each KPI completion level, the KPI system builder will determine a certain salary and bonus. This policy can be pre-determined by the leadership levels in the enterprise, the top management in the department, the person who builds the KPI system, or by the employees themselves agreeing with each other.
Usually, there will be an acceptance session to evaluate the work results periodically at the end of each evaluation period. The evaluation should be objective and comprehensive by incorporating, the opinions of the boss, colleagues, customers, and employees themselves.
Step 5: Adjust and optimize KPI
KPIs can be tracked and adjusted over time. Initially, review the KPIs that have just been created to ensure that the metrics are consistent. It may take the first few months for everything to be optimal but once the final KPI is in place, maintain it for at least a year.
Hopefully, through the above article, businesses, employers, as well as human resources, clearly understand how to evaluate KPIs and use this assessment tool effectively.
Contact Us
Hotline: (+84) 353 111 265
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/Aniday/
FB Page: https://www.facebook.com/aniday.com/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/Aniday4.0/
Aniday's HR Services
Headhunting Service
Find and recruit quality candidates in just 1 week! Supported by 40,000 experienced headhunters in IT, Finance, Marketing… capable of recruiting in any region.
Headhunting Service ➔Employer of Record (EOR) Service
On behalf of your business, we recruit employees and handle payroll without the need to establish a company in markets such as Vietnam, Singapore, Malaysia, India, Indonesia…
Employer of Record (EOR) Service ➔