Case Analysis for Consulting Interviews: A Practical Framework
If you are applying for a consulting job, you probably know that a case analysis interview is a crucial part of the selection process. In this type of interview, you are expected to use structured thinking to solve a business problem presented by the interviewer.
But how do you develop structured thinking and apply it to different cases? Do you need to memorize hundreds of frameworks and hope that one of them fits the case?
The answer is no. Memorizing too many frameworks is not only inefficient, but also risky. You may end up using a wrong or irrelevant framework, or worse, sounding like a robot who just recites a formula.
What you need is to master a few frameworks that can cover most of the case scenarios, and then use them flexibly and creatively according to the specific problem.
In this blog post, we will introduce three practical frameworks that can help you analyze cases in three common application scenarios: macroeconomic and industry, industry competition and company strategy, and specific management.
PEST Model: Analyze the Macro Environment
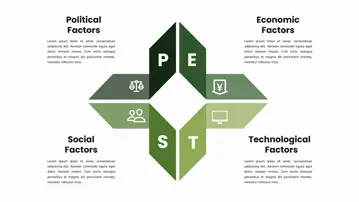
The PEST model is a framework that helps you understand how the macro environment affects an industry or a company. The macro environment consists of four aspects: politics, economy, society and technology. By taking the first letter of each aspect, we get the acronym PEST.
The PEST model can help you answer questions such as:
-
How does government policy affect the demand for a product or service?
-
How does the economic situation influence consumer behavior and purchasing power?
-
How does the social trend shape the customer preference and expectation?
-
How does technological development create opportunities or threats for a company or an industry?
When using the PEST model, you need to think about each aspect in relation to the case problem. For example, if you are analyzing the market potential of a new electric car, you may consider:
-
Political: What are the regulations and incentives for electric vehicles in different countries or regions?
-
Economic: What are the income levels and disposable incomes of potential customers? How does the oil price affect the demand for electric vehicles?
-
Social: What are the environmental awareness and attitudes towards electric vehicles among different segments of customers?
-
Technological: What are the current and future technologies that can improve the performance, cost and convenience of electric vehicles?
Porter’s Five Forces Model: Analyze the Industry Competition
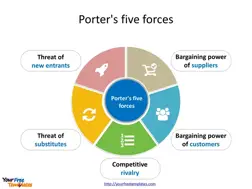
The Porter’s five forces model is a framework that helps you analyze the competitive situation of an industry in a market, and then evaluate the profitability and attractiveness of this industry.
The five forces are: direct competition within the industry, bargaining power of upstream suppliers, bargaining power of downstream customers, threat of new entrants and threat of substitution.
The Porter’s five forces model can help you answer questions such as:
-
How intense is the rivalry among existing competitors in the industry?
-
How much bargaining power do suppliers have over the industry players?
-
How much bargaining power do customers have over the industry players?
-
How easy or difficult is it for new entrants to enter the industry?
-
How likely is it for customers to switch to alternative products or services from other industries?
When using the Porter’s five forces model, you need to consider some key questions for each force. For example, if you are analyzing the competitive landscape of online food delivery platforms, you may consider:
-
Direct competition: How many platforms are there in the market? What are their market shares, growth rates and profitability? What are their strengths and weaknesses? How do they differentiate themselves from each other?
-
Bargaining power of suppliers: How many restaurants are there in the market? How dependent are they on the platforms? How much commission do they pay to the platforms? How loyal are they to one platform or another?
-
Bargaining power of customers: How many customers are there in the market? How price-sensitive are they? How loyal are they to one platform or another? How easy is it for them to switch platforms?
-
Threat of new entrants: What are the entry barriers for new platforms? How much capital, technology and network effects do they need? How can they attract restaurants and customers from existing platforms?
-
Threat of substitution: What are the alternatives for customers who want to order food online? How convenient, affordable and satisfying are they compared to online food delivery platforms?
Marketing 4P Model: Analyze Specific Management

The marketing 4P model is a framework that helps you analyze specific management problems such as evaluating existing solutions or designing marketing solutions. The 4P stands for product, price, place and promotion.
The marketing 4P model can help you answer questions such as:
-
What is the product positioning, feature and target customer segment?
-
What is the pricing strategy that maximizes revenue and profit?
-
What is the distribution channel and geographic area that reaches the most potential customers?
-
What is the communication and promotion method that raises awareness and interest among customers?
When using the marketing 4P model, you need to design or evaluate each element according to the case problem. For example, if you are analyzing the marketing strategy of a new social media platform that specializes in sarcasm, you may consider:
-
Product: What is the unique value proposition of the platform? How does it differ from other social media platforms? What are the main functions and features of the platform? Who are the target users and what are their needs and pain points?
-
Price: How does the platform generate revenue and profit? Is it based on subscription, advertising, commission or other models? How much does it charge users or advertisers? How does it compare to competitors or substitutes?
-
Place: How does the platform distribute its product and service to users? Is it through web, mobile app, email or other channels? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each channel? Which geographic markets does it focus on and why?
-
Promotion: How does the platform communicate and promote its product and service to users? Is it through social media, word-of-mouth, influencer marketing or other methods? What are the key messages and tones of the platform? How does it attract and retain users?
Conclusion
These are the three frameworks that I recommend you to master for your consulting case interview. Of course, these frameworks are not exhaustive or exclusive. You can always modify them or combine them according to the specific case problem.
The most important thing is to use them as a guide, not a rule. You need to apply them with logic, creativity and common sense. You also need to practice a lot of cases to improve your skills and confidence.
Aniday's HR Services
Headhunting Service
Find and recruit quality candidates in just 1 week! Supported by 40,000 experienced headhunters in IT, Finance, Marketing… capable of recruiting in any region.
Headhunting Service ➔Employer of Record (EOR) Service
On behalf of your business, we recruit employees and handle payroll without the need to establish a company in markets such as Vietnam, Singapore, Malaysia, India, Indonesia…
Employer of Record (EOR) Service ➔