100+ The opportunity to introduce the job of the Category UI/UX Designer
UI/UX Designer Jobs - High-Paying Roles
UX stands for “User Experience” design, meanwhile, UI stands for “User Interface” design. Both elements are essential to delivering a finished product, and they are seen to be combined as they are two closely connected professions that frequently work hand-in-hand.
Let's go over everything you need to know about UX/UI design.
1. What is the difference between UX and UI design?
UX Design
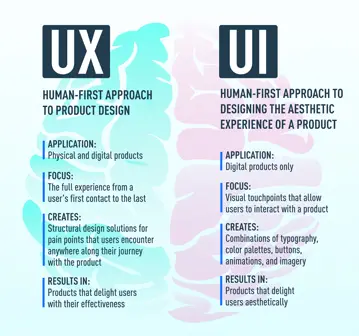
UX design prioritizes the human aspect of product design, which aims to create products that are both easy and enjoyable to use.
UX design takes into account the factors that influence how a user interacts with a good or service, how these factors affect the user's emotions, and how simple it is for the user to perform the activities they want to complete. This could refer to the ease of use of an online checkout process or the tactile quality of a tangible product in your hands.
"Every facet of the end-user engagement with the business, its services, and its products is included in the user experience." — Don Norman, a UX architect and cognitive scientist.
UI Design
Within UX, UI Design is an essential subset. Although they both aim to give the user a satisfying experience, UI Design is a whole different step in the process.
The user's visual experience is the main focus of UI design. It establishes how a user engages with an interface, whether a website, an app, or an e-commerce store. It all comes down to how the user uses various visual touchpoints to move from point A to point B. Imagine scrolling through photos or pressing a button.
A good interface requires the user to think about it very little. Think about the best app: the end users know it's user-friendly and easy on the eyes. They don't have to spend a lot of time figuring out how to move from point A to point B when they first install it.
2. Who are UX/UI Designers?
A UX designer makes sure a product makes sense and is easy to use, allowing the user to move from one task to the next without difficulty. A UI designer, on the other hand, is concerned with making sure that every page or screen graphically reflects this rational route.
To create seamless user experiences for goods, services, and procedures, UX designers integrate strategy, design, product development, and market research. By establishing a connection with the client, they enable the business to better comprehend and meet their requirements and expectations.
A UI designer's responsibility is to build the visual elements and their interaction qualities that enable a user to navigate through all of the displays that they will encounter. In this, the UI designer is essential. They consider the human user and the functioning of the mind. To direct the user, they make use of elements like color, spacing, and patterns.
3. What do UX designers do?
The following are typical day-to-day tasks and responsibilities for a UX designer:
-
Designing: Identifying design flaws, creating use cases, and proposing improvements for digital products to ensure functionality across browsers and systems.
-
Usability testing: test products through various methods like running tests on every URL of a website or application to uncover flaws. They also let consumers interact with prototypes to assess usability and functionality before launch, gathering valuable feedback essential for development.
-
User analysis and strategy formulation: researching the target market and competitors' products to understand user needs and behaviors. This research, often conducted through focus groups, interviews, and questionnaires, helps identify market gaps, and then they use these findings to create a content creation plan
-
Prototype and wireframe design: creating basic designs (wireframes) to illustrate user interaction and navigation. These serve as templates for the product's information architecture. High-fidelity prototypes are then developed for testing and feedback, resembling the final product to identify areas for improvement.

4. What do UI designers do?
A UI design expert may be in charge of all of the following throughout this design phase:
-
Establishing and upholding a visual language, or style guide, to guarantee uniformity throughout.
-
Creating every screen a user could interact with, choosing layouts and visual components that would contribute to the most user-friendly experience possible
-
Creating each user interface (UI) element's interactive design.
-
Making animations
-
Ensuring that a design will function properly on a variety of screen sizes
5. Which skills are important for UX/UI Designers?
A UX/UI designer needs to possess both technical and creative talents.
-
User research: it enables them to comprehend the requirements and preferences of their target audience.
-
Graphic design: they should be skilled with a variety of graphic design programs, have a solid understanding of design, and be able to construct aesthetically pleasing interfaces.
-
Optimizing readability: they should also know how to construct interactive components like buttons, menus, and icons, as well as how to arrange information and content so that it is easy to traverse.
-
Prototyping: having the ability to prototype is also crucial since it lets them test ideas and get input from users.
-
Critical thinking: helps them come up with original solutions for more challenging issues.
-
Adapting to change: To stay competitive in this field as it continues to change, UI/UX designers must constantly concentrate on picking up new skills and staying up to date with emerging technology and design trends.








